Global sanctions policy: what you need to know
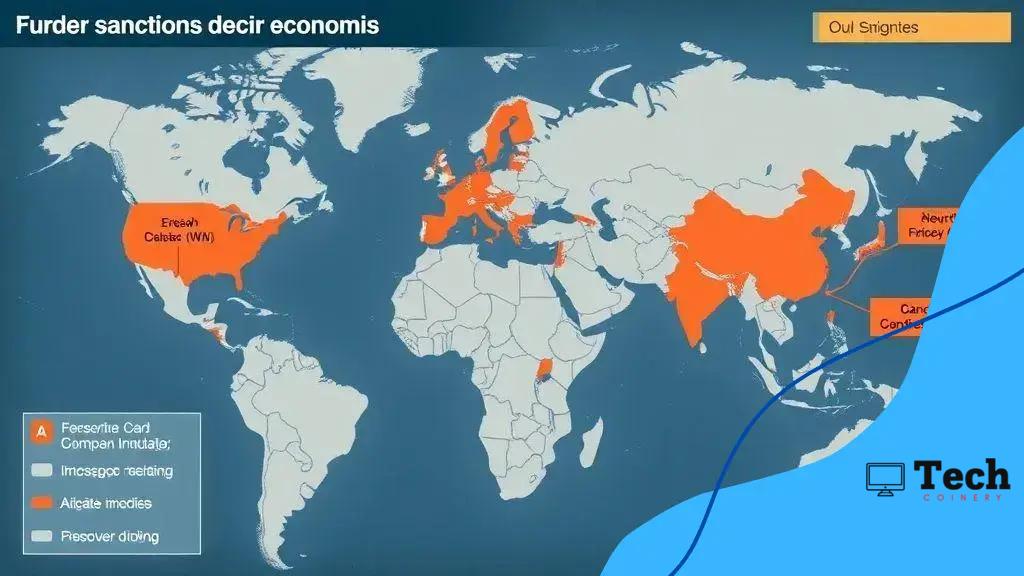
Global sanctions policy involves economic, diplomatic, and military measures imposed by nations to influence the behavior of targeted countries, aiming for political change while often impacting innocent citizens.
Global sanctions policy plays a vital role in shaping diplomatic and economic relations. Have you ever wondered how these measures influence nations and global commerce? Let’s dive into the complexities and impacts of sanctions.
Understanding the concept of global sanctions
Understanding global sanctions is essential in today’s interconnected world. These measures are designed to influence and regulate national behavior through economic and diplomatic pressures. When countries face issues such as aggression, human rights violations, or terrorism, the international community often responds with sanctions.
What Are Global Sanctions?
Global sanctions refer to various restrictions imposed by countries or international organizations on another nation. The goal is to alter the targeted country’s actions or policies without resorting to military force.
- Economic sanctions: Limit trade and investment.
- Diplomatic sanctions: Reduce or cut off diplomatic relations.
- Military sanctions: Restrict arms sales or military assistance.
- Travel bans: Prohibit specific individuals from entering countries.
These measures can be comprehensive or targeted. Comprehensive sanctions restrict all trade, while targeted sanctions focus on specific individuals or sectors.
How Do Sanctions Work?
Sanctions work by applying pressure to the economy and international standing of the sanctioned country. The hope is that this pressure will lead to a change in behavior. For example, if a country faces economic hardship due to sanctions, it may reconsider its policies.
Moreover, sanctions can signal disapproval from the global community, pressuring leaders to take action. However, they can also have unintended consequences, often affecting ordinary citizens more than political leaders.
Understanding these dynamics is crucial as they shape global politics and international relations. As nations navigate these complex relationships, the role of global sanctions continues to evolve, reflecting changes in international norms and policies.
The historical context of sanctions
The historical context of sanctions helps us understand their significance today. Sanctions have been used for centuries as tools of international diplomacy. Ancient examples show how nations would cut off trade to punish others for aggressive actions.
In modern history, the use of sanctions took on new forms, especially after the two World Wars. Global conflicts highlighted the need for international agreements and responses. The League of Nations, and later the United Nations, began implementing sanctions as collective measures against aggressor states.
The Cold War Era
During the Cold War, sanctions became a part of the geopolitical strategy. Nations like the United States used them against countries that opposed their interests or aligned with the Soviet Union. These sanctions were not just punitive; they aimed to deter specific behaviors and influence political changes.
- Trade embargoes were common during this time.
- Arms restrictions targeted countries involved in conflicts.
- Economic sanctions affected nations with poor human rights records.
As we moved into the 21st century, the nature of global sanctions evolved even further. The September 11 attacks prompted countries to impose sanctions on nations suspected of supporting terrorism. Today, sanctions are often used not just for military aggression, but also for promoting human rights and democracy.
Recent Developments
Recent events such as the situation in Ukraine have shown that sanctions continue to play a crucial role in global politics. Countries are increasingly using sanctions to address issues like territorial disputes and military interventions. The impact of these sanctions can be extensive, affecting not just governments but also populations.
Understanding the historical context of sanctions gives us valuable insights into their role in shaping international relations and the ongoing discussions around their effectiveness and moral implications.
Types of sanctions and their applications
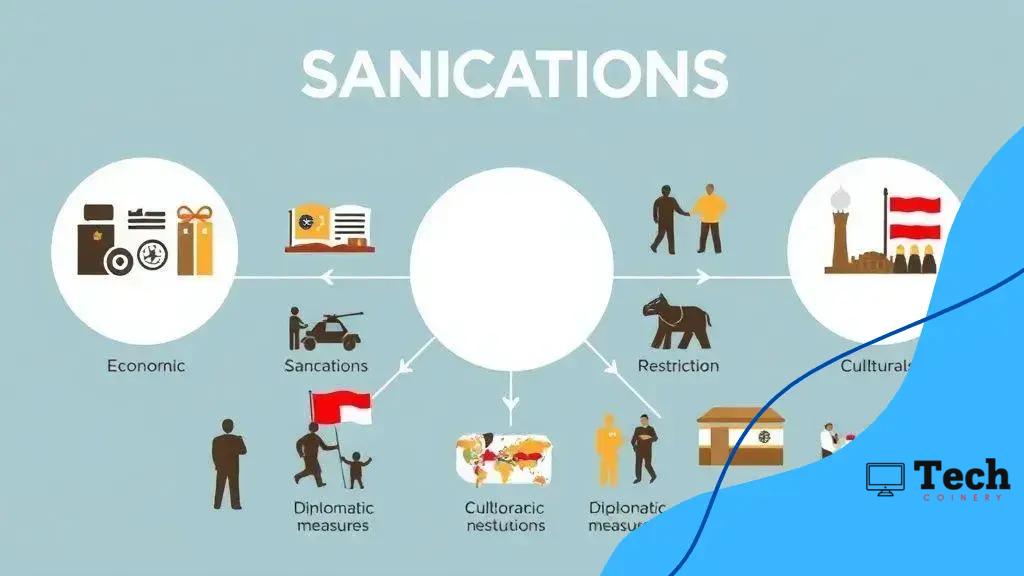
There are several types of sanctions that countries and international organizations use to achieve their political and economic goals. Understanding these types helps clarify their applications in global affairs. Each type serves different purposes and can target various aspects of a nation’s economy and governance.
Economic Sanctions
Economic sanctions are the most common type. They restrict trade and financial transactions with the targeted nation. These sanctions can lead to significant economic hardship and are usually aimed at persuading governments to change specific policies.
- Trade embargoes limit imports and exports.
- Asset freezes prevent targeted individuals or governments from accessing funds.
- Investment bans stop foreign investment into the sanctioned country.
Such measures can cripple a nation’s economy, as they cut off vital resources and financial support.
Diplomatic Sanctions
Diplomatic sanctions involve reducing or cutting off diplomatic relations. This type might include withdrawing ambassadors or limiting diplomatic communication. These measures serve to express disapproval and isolate the targeted country from international dialogues.
Military Sanctions
Military sanctions can take the form of arms embargoes, restricting the sale of weapons to certain countries. These sanctions aim to deter military aggression or conflicts and encourage disarmament.
Social and Cultural Sanctions
Lastly, social and cultural sanctions focus on limiting participation in international events. These may include bans from the Olympics or other global competitions and affect a country’s international reputation and prestige.
Ultimately, the effectiveness of types of sanctions can vary significantly based on the goals of the imposing country, the resilience of the targeted nation, and the level of international support.
Impact of sanctions on global trade
The impact of sanctions on global trade is significant and multifaceted. When sanctions are imposed, they disrupt the flow of goods and services between countries. This disruption can lead to economic declines and shifts in trade patterns.
Sanctions typically target key sectors, such as energy, finance, and agriculture. For example, when a country faces sanctions on its oil exports, its income drops dramatically. This not only affects the targeted country but also has ripple effects on global markets and economies that rely on those resources.
Trade Relationships
Moreover, sanctions can alter long-standing trade relationships. Countries seeking to bypass restrictions may form new alliances with nations outside the sanctioning body. This can lead to the emergence of alternative trading partners and routes.
- Countries may import from different regions.
- New markets can open for non-sanctioned countries.
- Small nations may leverage new opportunities for trade.
As nations adapt to sanctions, they often seek new ways to maintain economic stability. This can include developing new domestic industries or increasing exports to friendly nations. However, the overall effect of sanctions usually results in a contraction of trade.
Price Fluctuations
Sanctions can also lead to price fluctuations in affected commodities. For instance, if a major oil producer faces sanctions, global oil prices might spike due to reduced supply. This price volatility can create uncertainty in the market, affecting consumers and businesses alike.
Overall, the impact of sanctions on global trade underscores the delicate balance of international economics. While meant to enforce political change, the consequences can lead to unintended hardships for both the targeted nations and their global trading partners.
Evaluating the effectiveness of sanctions
Evaluating the effectiveness of sanctions is crucial for understanding their role in international relations. Different sanctions have varying levels of success, and their impacts can be complex. An effective sanction is one that achieves its intended goals without causing excessive harm to innocent populations.
There are several factors to consider when assessing how well sanctions work. One key aspect is whether the sanctioned country changes its behavior in response to the imposed measures.
Measuring Behavioral Changes
To evaluate sanctions, analysts often look for specific behavioral changes, such as:
- Policy shifts by the government in question.
- Compliance with international norms.
- Reduced military aggression or human rights violations.
If any of these changes occur, it indicates that the sanctions might be having an effect. However, this can take time and relies heavily on the willingness of the targeted government to respond.
Unintended Consequences
Sanctions can also produce unintended negative effects. Sometimes they may strengthen the resolve of a government to resist outside pressure. In such cases, instead of yielding to demands, regimes may rally domestic support by portraying the sanctions as foreign aggression.
Additionally, economic sanctions often hurt the general population more than the political elite. For instance, restrictions on imports can lead to shortages of essential goods, harming everyday citizens instead of affecting the intended political targets.
International Support
The effectiveness of sanctions also hinges on the level of international support. Unified sanctions from multiple countries tend to be more effective than unilateral ones. When a large group of nations imposes sanctions, the target country faces greater pressure to comply.
Ultimately, evaluating the effectiveness of sanctions requires a nuanced understanding of both their intended and unintended consequences. As sanctions evolve, continuous analysis is essential to determine their true impact on global politics.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions About Global Sanctions Policy
What are global sanctions?
Global sanctions are measures imposed by countries or international organizations to influence a nation’s behavior, often in response to aggression or human rights violations.
How do sanctions impact global trade?
Sanctions disrupt trade flows, leading to economic declines and changing trade patterns, impacting not only the targeted nation but also global markets.
What types of sanctions exist?
There are several types, including economic sanctions, diplomatic sanctions, military sanctions, and social or cultural sanctions.
How can we evaluate the effectiveness of sanctions?
Effectiveness can be evaluated by measuring behavior changes in the targeted country, looking for compliance with international norms, and assessing the overall economic impact.






