Green infrastructure plan: transforming urban spaces

A green infrastructure plan integrates natural systems into urban settings to manage stormwater, improve air quality, and enhance community spaces, leading to sustainable and resilient cities.
A green infrastructure plan is crucial for creating sustainable urban environments. Have you ever wondered how cities can thrive while reducing their environmental impact? Let’s dive into what this means for our communities.
Understanding green infrastructure
Understanding green infrastructure is essential for building resilient and sustainable cities. It involves using nature to manage water, improve air quality, and enhance community spaces. By integrating green elements into urban planning, we can create healthier environments.
What is Green Infrastructure?
Green infrastructure refers to a network of natural and semi-natural systems that provide multiple benefits to urban areas. This approach leverages green spaces and ecosystems to address various challenges, such as flooding, heat islands, and biodiversity loss. It represents a shift from traditional grey infrastructure to more ecological solutions.
Key Benefits
- Improved Water Management: Green infrastructure captures stormwater, reducing runoff and improving water quality.
- Enhanced Urban Aesthetics: Parks and green roofs create more pleasant and visually appealing urban environments.
- Climate Resilience: By providing shade and cooling, green spaces help mitigate the effects of climate change.
Furthermore, green infrastructure can significantly improve public health. Access to parks and green spaces encourages outdoor activities, promoting physical well-being. Additionally, greenery can reduce stress and enhance mental health by providing a connection to nature.
As cities continue to grow, the importance of integrating green infrastructure cannot be overstated. It plays a critical role in creating sustainable communities that adapt to changing environmental conditions. By understanding its principles, city planners and communities can work together to implement effective solutions for a greener future.
Benefits of implementing a green infrastructure plan
Implementing a green infrastructure plan offers numerous advantages for urban areas. These benefits span environmental, economic, and social aspects, making cities more resilient and livable. Understanding these can encourage communities to adopt and invest in green solutions.
Environmental Advantages
First and foremost, green infrastructure enhances natural ecosystems. It helps in managing stormwater more effectively, thus reducing flooding risks. Additionally, it can improve air quality by filtering pollutants and absorbing carbon dioxide. Biodiversity in urban areas also increases through green roofs, parks, and community gardens.
Economic Benefits
Economically, green infrastructure can be a cost-saving measure. It often requires less maintenance than traditional grey infrastructure. Cities can save on energy costs, while property values tend to rise due to the presence of green spaces. Moreover, jobs are created in landscaping, construction, and ecological management.
- Increased Property Values: Properties near green spaces often sell at higher prices.
- Job Creation: Implementation creates jobs in various sectors related to maintenance and development.
- Cost Savings: Reduced infrastructure maintenance and energy savings.
Socially, green infrastructure provides vital spaces for recreation and relaxation. These areas encourage community engagement and improve mental health by offering a natural escape from urban life. Parks and green areas often become community hubs where people gather and interact.
Key components of an effective green infrastructure plan
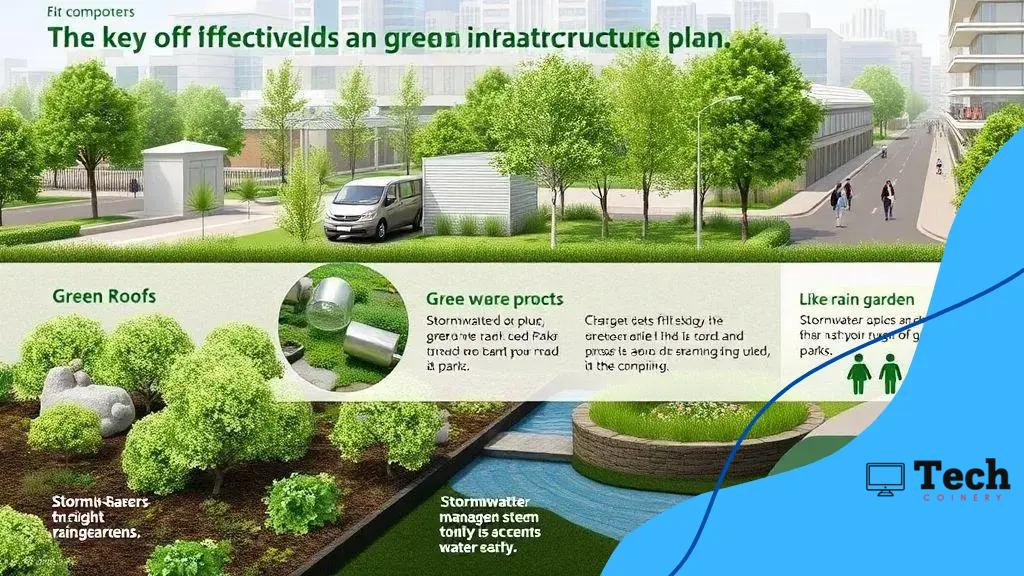
Creating an effective green infrastructure plan involves several key components that work together to enhance urban environments. These components address various issues, such as water management, air quality, and community engagement.
Green Spaces
One of the main components includes the incorporation of green spaces like parks, gardens, and green roofs. These areas not only enhance the aesthetics of a city but also provide vital habitats for wildlife. Well-designed green spaces can manage stormwater effectively, minimizing flood risks.
Stormwater Management Systems
Effective stormwater management systems are essential in any green infrastructure plan. Techniques such as rain gardens, permeable pavements, and bioswales allow water to be absorbed naturally, reducing runoff and filtering pollutants before they enter local water bodies.
- Rain Gardens: These are landscaped areas that collect rainwater and allow it to soak into the ground.
- Bioswales: These channels are designed to direct and treat stormwater using vegetation and soil.
- Permeable Pavements: These surfaces allow water to pass through, reducing surface runoff.
Additionally, urban forestry is another crucial element. Trees play a significant role in improving air quality and reducing urban heat. They provide shade, which can lower energy costs and enhance the livability of urban areas. Promoting tree planting initiatives is vital for expanding tree canopies.
Moreover, green roofs and walls not only improve building insulation but also offer spaces for urban agriculture. This can increase local food production and promote community connections. Involving community stakeholders in the planning process is also essential. Their support and input can lead to more successful and sustainable initiatives that reflect the needs of the community.
Challenges in developing green infrastructure
Developing green infrastructure presents various challenges that can hinder successful implementation. These obstacles can be technical, financial, or social, requiring strategic planning and community involvement.
Funding and Budget Constraints
One major challenge is securing adequate funding. Many cities face budget constraints that limit investment in green infrastructure projects. Traditional funding sources may not cover the costs associated with these initiatives. As a result, alternative financing methods, such as public-private partnerships, are often necessary but can be complex to establish.
Technical and Design Issues
Another challenge involves technical and design issues. Implementing green infrastructure requires specialized knowledge and expertise. Many urban planners may not have sufficient training in green design principles, which can lead to ineffective solutions. Additionally, integrating green features into existing infrastructure can be complicated, requiring careful planning.
- Maintenance needs: Green infrastructure often requires ongoing maintenance, which can be a burden for city budgets.
- Space limitations: Urban areas may lack sufficient space for parks and gardens.
- Regulatory hurdles: Zoning laws and regulations can restrict the implementation of certain green projects.
Community acceptance is also vital. Engaging the community in the planning process helps address concerns and gather support. Without community buy-in, projects may face significant resistance, leading to delays or cancellations. Educating residents about the benefits of green infrastructure can foster trust and encourage participation.
Additionally, long-term planning and commitment are necessary to ensure these projects are sustainable. Many green infrastructure projects take time to show results, which can challenge the patience of stakeholders looking for immediate benefits. Balancing short-term and long-term goals is crucial for success in implementing green infrastructure.
Case studies: successful green infrastructure projects
Exploring case studies of successful green infrastructure projects provides valuable insights into their impact and effectiveness. These projects highlight how cities can implement sustainable solutions that benefit the environment and communities.
New York City’s Green Roof Initiative
One notable example is New York City’s green roof initiative. The city has incentivized the installation of green roofs on commercial buildings. This initiative provides numerous benefits, including improved energy efficiency and enhanced stormwater management. Green roofs help reduce the urban heat island effect, making the city cooler in the summer.
Philadelphia’s Water Management Program
Another successful project is Philadelphia’s program to manage stormwater. The city has transformed streets and public spaces with bioretention areas, rain gardens, and green streets. This approach has significantly reduced the amount of stormwater runoff entering sewer systems. Furthermore, it has increased green space in neighborhoods, providing residents with recreational areas while improving air and water quality.
- Reduction in flooding: These projects have helped lessen the frequency and severity of urban flooding.
- Enhanced community spaces: Engaging the public with green spaces fosters healthier lifestyles and community bonds.
- Economic savings: Long-term savings have been recognized in reduced energy and water costs.
In Melbourne, Australia, the cultivation of urban forests has transformed city landscapes. This initiative has not only provided aesthetic benefits but also improved biodiversity. By planting native trees and creating green corridors, Melbourne has increased its tree canopy cover, enhancing the quality of life for residents.
These examples show that successful green infrastructure projects can be replicated in various contexts. By learning from these case studies, other cities can adopt similar initiatives tailored to their unique needs.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Green Infrastructure Plans
What are the main benefits of green infrastructure?
Green infrastructure improves air quality, manages stormwater, enhances urban spaces, and fosters community engagement.
How can cities fund green infrastructure projects?
Cities can use public-private partnerships, grants, and local taxes to secure funding for green infrastructure initiatives.
What are some examples of successful green infrastructure projects?
Examples include New York City’s green roof initiative and Philadelphia’s stormwater management program.
How does community involvement impact green infrastructure projects?
Community involvement is crucial for ensuring projects meet local needs and gain support, leading to successful implementation.






